Connect to a relay chain
This guide summarizes how to connect a parachain to a relay chain. It is intended to be a quick reference for when you are ready to deploy a parachain on a test or production network and have already performed similar steps in a local testing environment. If you haven't previously set up a local relay chain and connected a parachain to it, you should follow the steps in Prepare a local relay chain and Connect a local parachain before using this guide.
The guide highlights the following topics:
- How to obtain a unique identifier for your parachain
- How to register a parachain
- How to obtain a parachain slot
Before you can secure a slot on a relay chain, you must prepare some information about the parachain and provide this information to the relay chain that you want to connect to.
To prepare a parachain for connecting to a relay chain, you must successfully complete the following steps:
- Reserve a unique identifier on the specific relay chain that you want to connect to.
- Compile the WebAssembly runtime binary.
- Generate the genesis state from the chain specification for the parachain.
After you complete these steps to register the parachain for a specific relay chain, you can request a slot on that relay chain to add your parachain to the network. For testing purposes, you can acquire a slot on the relay chain using the Sudo pallet. For production networks, you can acquire a slot through auctions and crowdloans. After you secure a slot on a relay chain, the parachain can start producing blocks.
Reserve a unique identifier
You must have a unique identifier for a specific relay chain before you can perform any operation that involves your parachain or parathread. For example, you must have a unique identifier to load the WebAssembly blob, register the genesis state, create messaging channels to other parachains, or start a crowdloan.
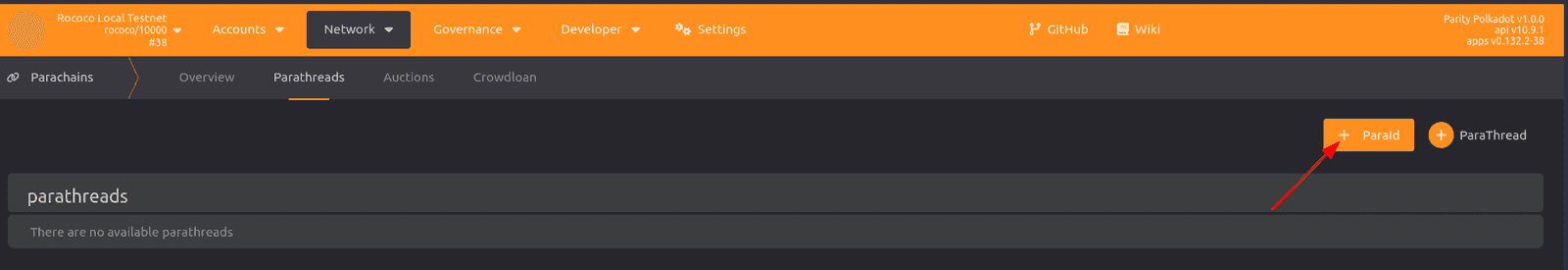
To reserve an identifier:
- Open the Polkadot/Substrate Portal in a web browser and connect to the WebSocket port for your running parachain node.
- Click Network and select Parachains.
-
Click Parathreads, then click +ParaID.
![Reserve a `ParaID`]()
-
Submit a transaction to reserve the ParaID for the relay chain that you want to connect to.
The transaction requires a deposit. The account you use to reserve the identifier is charged for the transaction and will be the origin account for the parathread associated with the identifier.
Note that the identifier can only be used with for the relay chain you are registering with and that you must specify the identifier to complete additional steps.
Customize the parachain specification
You must configure the chain specification for your parachain to use the identifier you have reserved. To perform this task, you must:
- Generate the chain specification as a plain text JSON file.
- Modify the chain specification in a text editor.
- Generate the modified chain specification in raw format.
To create the custom chain specification:
-
Generate the plain chain specification by running a command similar to the following:
./target/release/parachain-template-node build-spec --disable-default-bootnode > rococo-local-parachain-plain.jsonThe command in this example assumes that
rococo-localis the relay chain you have registered with in thenode/chan_spec.rsfile. -
Open the plain text chain specification file in a text editor and set the
ParaIDto theParaIDyou previously reserved.For example, open the
rococo-local-parachain-plain.jsonfile and modify two fields:// --snip-- "para_id": <your-reserved-identifier> , // --snip-- "parachainInfo": { "parachainId": <your-reserved-identifier> }, // --snip-- -
Generate the raw chain specification from your modified chain specification file by running a command similar to the following:
./target/release/parachain-template-node build-spec \ --chain rococo-local-parachain-plain.json \ --raw \ --disable-default-bootnode > rococo-local-parachain-raw.json
Save and distribute the raw chain specification
If you intend to let others connect to your network, you must build and distribute a deterministic runtime build for your network. For inforamtion about how to build a deterministic runtime, see Build a deterministic runtime.
By convention, chain specifications are in a /chain-specs folder that is published in the codebase fot your node.
For example:
- Polkadot includes these relay chain chain specifications under node/service/chain-specs
- Cumulus includes these parachain chain specifications under chain-specs.
It is good practice to commit the raw chain specification into your source before proceeding.
Obtain the WebAssembly runtime validation function
The relay chain also needs the parachain-specific runtime validation logic to validate parachain blocks.
You can run the export-genesis-wasm command on a parachain collator node to produce this WebAssembly blob.
For example:
./target/release/parachain-template-node export-genesis-wasm --chain rococo-local-parachain-raw.json > para-wasmGenerate a parachain genesis state
To register a parachain, the relay chain needs to know the genesis state for the parachain.
You can run the export-genesis-state command on a parachain collator node to produce the hex-encoded genesis state for the parachain.
For example:
./target/release/parachain-template-node export-genesis-state --chain parachain-raw.json > para-genesisStart the collators
You are now ready to start a collator node with a command similar to the following:
parachain-collator \
--alice \
--collator \
--force-authoring \
--chain parachain-raw.json \
--base-path /tmp/parachain/alice \
--port 40333 \
--rpc-port 8844 \
-- \
--execution wasm \
--chain <relay-chain-spec-json> \
--port 30343 \
--rpc-port 9977In this command, the arguments passed before the lone -- argument are for the parachain collator.
The arguments after the -- are for the embedded relay chain node.
Note that the relay chain specification should be the chain specification for relay chain you have registered with.
You should see the collator running and peering with relay chain nodes. However, the parachain won't be authoring parachain blocks yet. Authoring begins after the collator is registered on the relay chain.
Parachain registration
Depending on your target relay chain and the authorities there, you have options to register. Typically, you use Sudo transactions for testing and parachain auctions and crowdloans for production.
This guide only covers the using Sudo transactions.
Registration deposit calculation
Optionally, you can calculate the exact formulas for deposit calculation for Polkadot runtimes in the function:
pub const fn deposit(items: u32, bytes: u32) -> Balance {}You can find this function for each relay chain in the Polkadot repository. For example:
Register using sudo
To register the parachain on the relay chain using a sudo call.
- Open Polkadot/Substrate Portal in a browser and connect to the target relay chain.
- Click Developer and select Sudo.
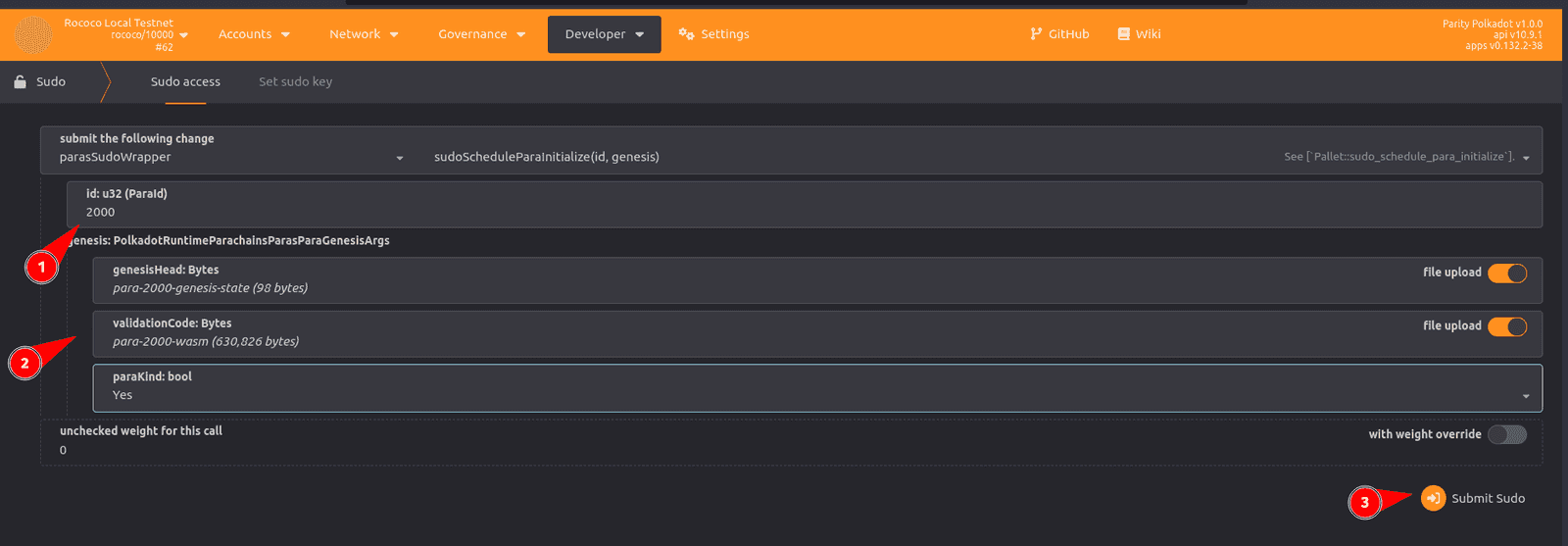
-
Select paraSudoWrapper, then select sudoScheduleParaInitialize(id, genesis) to initialize the reserved identifier at the start of the next relay chain session.
For the transaction parameters:
id: Type your reservedParaId.genesisHead: Click file upload and upload the genesis state you exported for the parachain. For this tutorial, select thepara-2000-genesisfile.validationCode: Click file upload and upload the WebAssembly runtime you exported for the parachain For this tutorial, select thepara-2000-wasmfile.paraKind: Select Yes.
![Set parameters for registration]()
- Verify the transaction is successful by clicking Network and selecting Explorer to view the
sudo.Sudidandparas.PvfCheckAcceptedevents in the list of recent events.
Registering using a slot lease
You can also use a Sudo transaction to force a slot lease.
To force a slot lease:
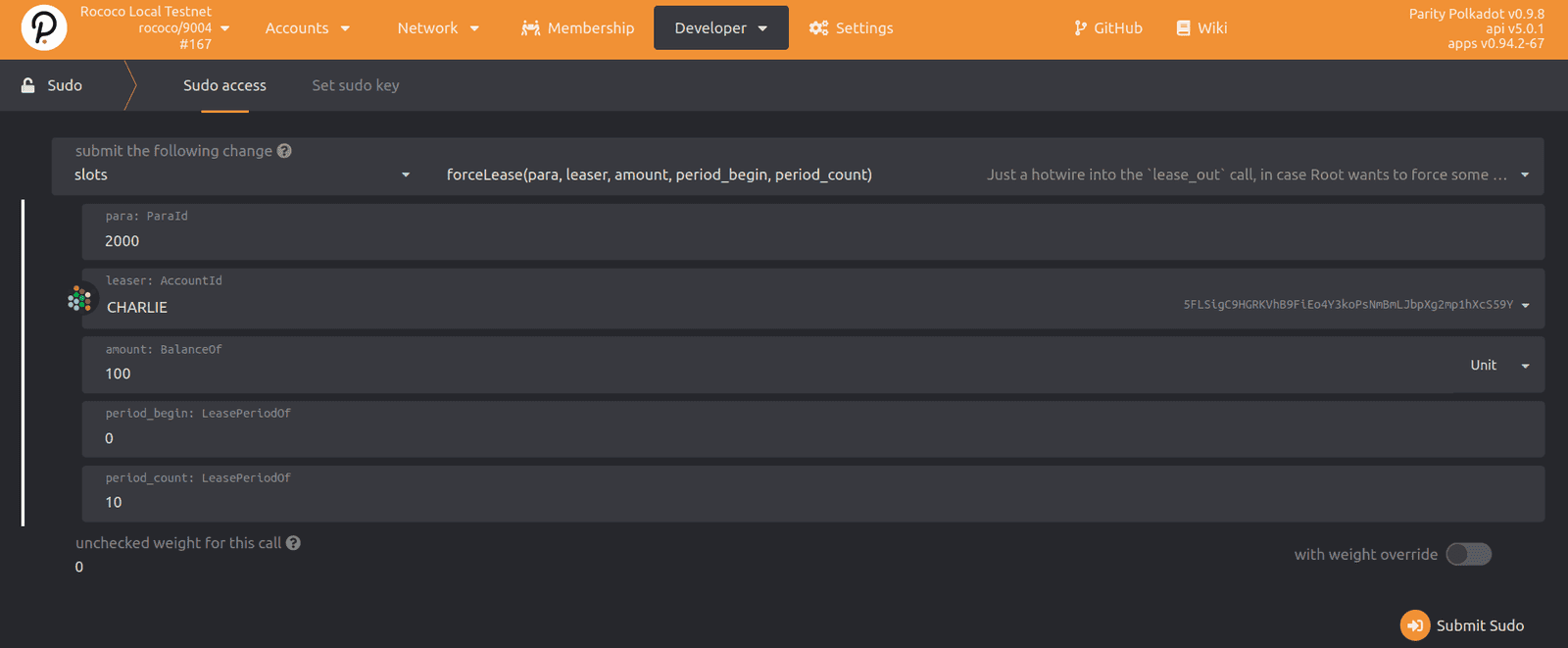
- Open Polkadot/Substrate Portal in a browser and connect to the target relay chain.
- Click Developer and select Sudo.
-
Select slots then select forceLease(para, leaser, amount, periodbegin, periodend).
![Sudo transaction to force a slot lease]()
For the transaction parameters:
period_begin: Specify the slot you want to start with. For example, the active slot0in a test environment.period_end: Specify a slot beyond the time you have set aside for testing the parachain. If you want to test onboarding and offboarding, you should select slot leases that have gaps.
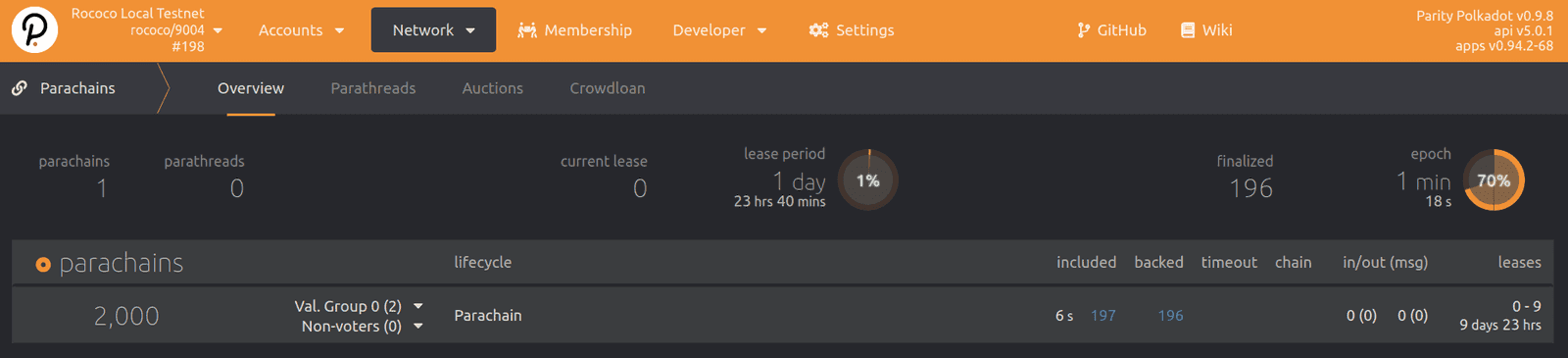
After the parachain is onboarded and block production starts, you should see information similar to the following for your parachain:
![View information about the parachain]()
Block production and finalization
The collator should start producing parachain blocks after the registration is successful and a new relay chain epoch has begun.
It can take a while for a new epoch to begin.
You can keep track of the parachains that are registered and their latest head data in the Polkadot/substrate Portal by clicking Network and selecting Parachains.