Deploy
Moving a project from a test network into production requires a clear view of your infrastructure and network operations. The topics in this section are intended to provide some guidance on how to deploy a parachain and how to prepare for network maintenance after you deploy. Before diving into specific deployments options and operations, however, there are a few important considerations that should act as the foundation for your deployment process. At a high level, you should apply the following general principles throughout all phases of your network deployment:
- Infrastructure operations should be code-driven and kept under version control.
- Security should be a central concern in all of your infrastructure decisions.
- Securing on-chain operations is critical to a successful deployment.
Build a code-driven infrastructure
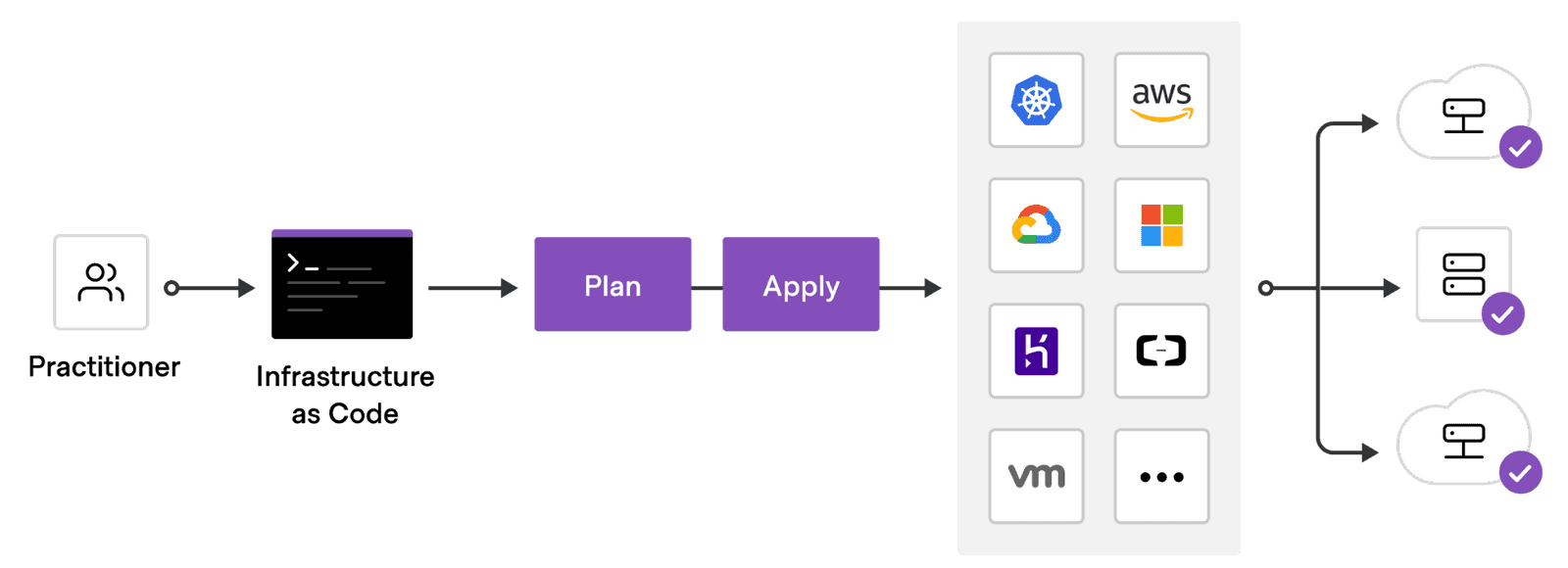
As a general rule, you should take an infrastructure-as-code approach to your deployment planning and preparation. All of the infrastructure components used to deploy the network should be written in code and managed through a version control system.
Following an infrastructure-as-code process helps to ensure that:
- Your infrastructure components are always in a known state.
- You can track changes, enforce reviews, and audit activity through version control.
- You can easily roll back to a known state, if needed.
- You can automate operations and won't need to perform manual tasks to redeploy.
Build security into the infrastructure
Security is one of the most important properties of a blockchain, so making your infrastructure secure by default should be a top priority when you plan to deploy a new network.
Having strict access control rules and blocking any non-required communication is a good starting point, but you should also consider how you can enhance security through the following:
- Log monitoring
- Bastion hosts for access
- Two-factor authentication for secure shell (ssh) access
Build security into chain operations
In addition to the infrastructure that your network relies on, it's important to keep on-chain operations as secure as possible. For example, by setting up your chain to use cold, warm, and hot keys, you can limit the damage that the compromise of a session key could do. The following diagram illustrates using keys for different operations to help prevent funds from being stolen.
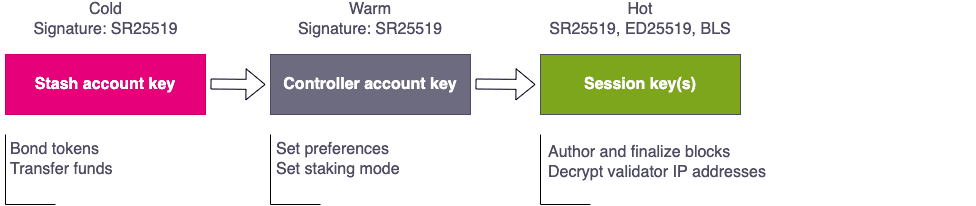
You can also use multi-signature accounts on offline devices to improve security and to provide an on-chain audit trail of all actions. The record of on-chain activity could then be used to send alert notification for specific on-chain actions.
Proxy accounts also let you limit the permission that an account or multi-signature account has on a particular target account. For example, you might use a proxy account to specify that a multi-signature staking controller account can only execute staking transactions and the transaction can only be executed if three of the five people that make up the multi-signature account approve.
